

Star Melody
for Wrist Rehabilitation
01 Concept
Melody of the Star Fragments is a simple game on Meta Quest.
It aims to exercise wrist flexibility and range of motion (ROM).
The game transforms rehabilitation exercises into a fantastical, immersive musical journey with progressively increasing difficulty.

✨ Here's a YouTube Video of our wonderful project
If the video seems shy, give it a second to show up!
02 Interaction Design & Wrist Rehab
Traditional Active Wrist Exercises
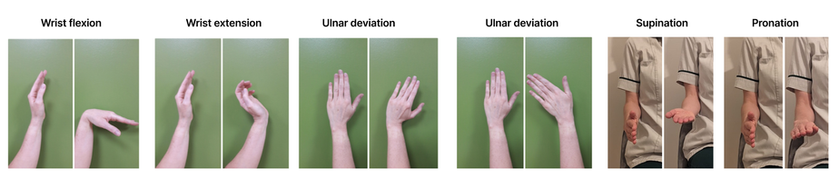
Exercises are completed slowly within a comfortable, symptom‑limited range.
A common dosage is 5–10 repetitions, 4–5 times per day, holding each end‑range for ~5 seconds, and progressing as symptoms allow.
Interaction Design & Wrist Rehab in Game

What Participants Say
04 Reflections

We often assume that full immersion in VR is always ideal.
But,
what if the user doesn’t want to be fully immersed?
What if they need to pause at any time,
or stay aware of their surroundings?
This question becomes especially important in serious games, where functionality matters more than entertainment.
It’s a bit like choosing how to exercise:
some people go to the gym to run on a treadmill,
others prefer to just run home after class.
Onboarding and guidance matters.
Headset setup and in-app guidance are critical.
Guidance must be clear and also noticeable.
A 360-degree scene increases the risk of cognitive overload and missed cues.
03 Research Findings
Mode-specific strengths and limitations
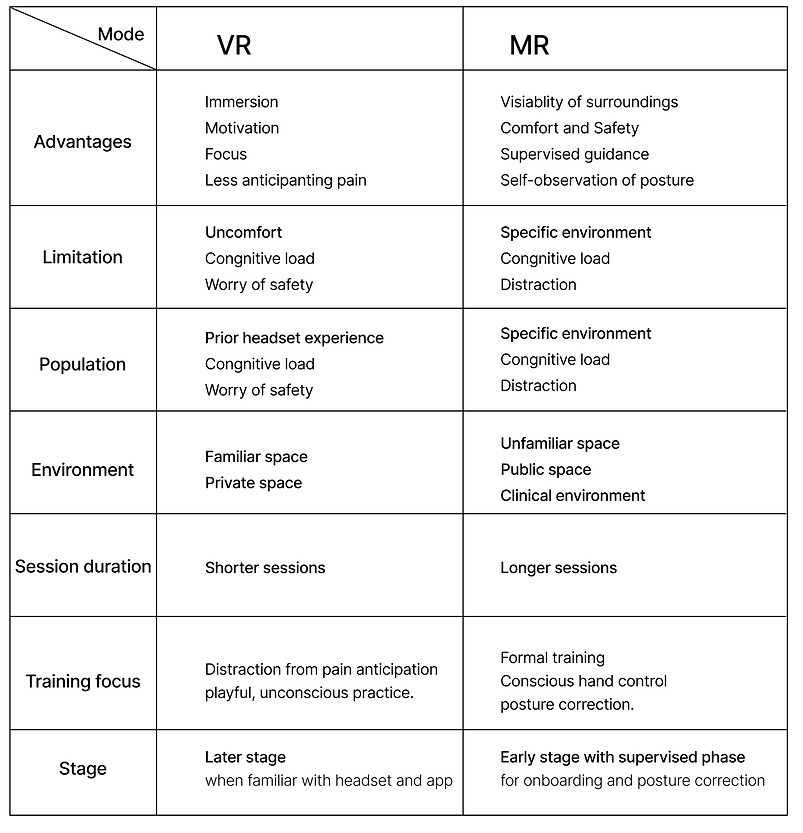
A progressive pathway——“MR first, then VR"
MR first during early supervised training, followed by VR during home-based consolidation, leveraging immersion to maintain focus and motivation.
In early, supervised, or public contexts, MR provides direct guidance, prioritizing safety and control.
As training transitions to the home consolidation phase, VR can then be leveraged to deliver immersion, rapid engagement, and sustained motivation for active training.
Future Design Guideline for two mode
Building on the distinct functions of VR and MR and the need to accommodate diverse rehabilitation contexts, the two modes should differ in visual and game design while offering multiple options.
A gradual transition from MR to VR, moving from realistic to more imaginative elements, may help users adapt progressively.
MR mode
For MR, visual parameter presets can support comfort across different rehabilitation settings:
(1)Defaut preset: brightness −0.2 to −0.3, saturation −0.4 to −0.5, covering the comfort–safety–focus balance for most users.
(2)Brighter preset: brightness 0.2 to 0.3, saturation −0.4 to −0.5, for users preferring slightly brighter scenes.
(3)Custom adjustment panel: interactive methods for parameter control remain to be evaluated for usability.
In MR, only essential virtual elements should be displayed, with clear visual styles. Overly complex overlays should be avoided, as they may reduce legibility and recognition.
VR mode
For VR, the design can gradually transition from realistic to more surreal visual styles, reducing cognitive overload or insecurity in early sessions.
(1)**Early levels**: simplified visuals with fewer virtual elements, grounded in familiar scenes (e.g., natural environments) and realistic embodied models, to reduce fear or disorientation for new users.
(2)**Later levels**: imaginative and surreal scenes (e.g., cosmic or starry environments).
VR may also incorporate narrative, props, environments, or avatar customization as unlockable rewards to strengthen long-term motivation.
Mode switching and parameter adjustment function as a bridge between VR and MR.

Most preferred darker and less saturated visuals, with saturation values around −0.45 being common.
Accordingly, for MR-based indoor rehabilitation without direct interaction with the physical environment, systems should provide both manual adjustment and one-click presets, and could eventually suggest optimal settings automatically based on context. For example, the system may recommend more visible settings when external guidance is expected, or darker presets when immersion and focus are prioritized.
05 About Me
I’m a creative technologist with a background in architecture and XR interaction.
I believe stories and human warmth give soul to products.
I am passionate about how creativity and technology can shape new experiences and socially meaningful solutions.

